ADHD Support and Management

Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a condition that can influence focus, organisation, and emotional regulation. Adequate support usually combines several approaches, tailored to each individual’s needs. In line with NICE guidance, structured psychological strategies, lifestyle adjustments, and, where appropriate, medical treatment may be considered as part of a comprehensive care plan.
Behavioural and Psychological Strategies
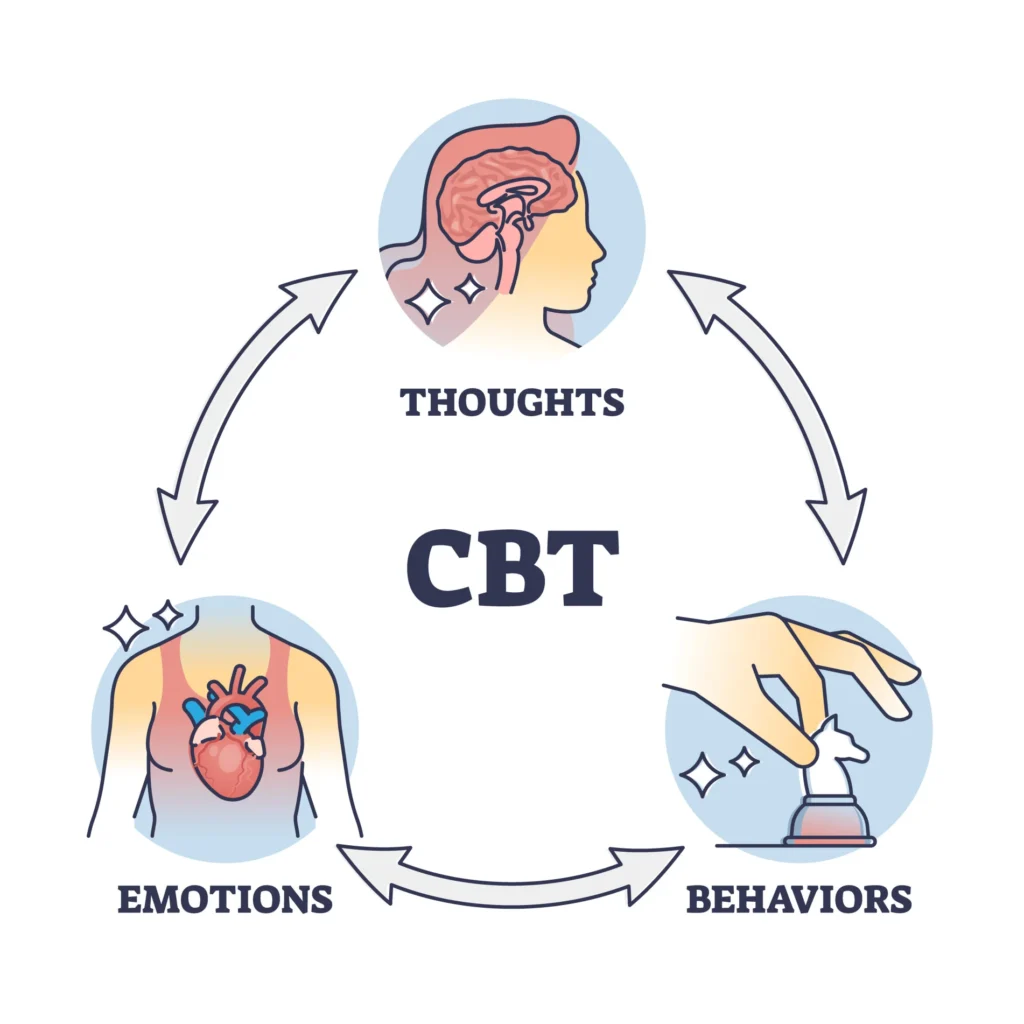
Structured routines, coaching, and behavioural techniques can help people manage day-to-day tasks more effectively. Approaches such as cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) or skills-based coaching may provide tools for managing impulsivity, improving organisation, and strengthening coping strategies.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Healthy daily habits can play a big role in managing ADHD symptoms.
- Regular exercise supports focus and reduces restlessness.
- Balanced nutrition provides steady energy throughout the day.
- Good sleep routines help maintain attention and emotional balance.
- Limiting screen time and encouraging social interaction can also have a positive impact.
Educational and Workplace Support
For children and adolescents, adjustments at school can help them thrive. These may include extra time for tests, a quieter environment for study, or the use of technology to aid learning. Adults may benefit from workplace accommodations such as structured deadlines, flexible working, or supportive planning tools.
Certain brain chemicals, known as neurotransmitters, are thought to play a role in attention, focus, and emotional regulation. Research suggests that differences in these brain systems may contribute to the symptoms of ADHD. Treatments, whether behavioural, lifestyle-based, or medical, aim to support a healthier balance in these processes, helping individuals better manage challenges with concentration and impulsivity.

The Role of Medical Treatment
In some cases, healthcare professionals may discuss whether medication could be an option as part of an overall support plan. The choice to use medication is highly individual and always depends on factors such as age, needs, and overall health.
Decisions about this are made in consultation with a qualified clinician, who will weigh up potential benefits alongside possible risks. Regular appointments with you’re clinician are essential to monitor the effectiveness of your treatment and make any necessary adjustments.
Understanding ADHD and the Brain
Research suggests that ADHD is linked to differences in how certain brain systems regulate attention, focus, and behaviour. Support strategies aim to strengthen these systems, helping people better manage challenges with concentration, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
Key Takeaways
- ADHD management is most effective when support is tailored to the
individual. - A combination of behavioural strategies, lifestyle changes, educational
support, and, where appropriate, medical treatment may be considered. - Decisions about medical treatment should always be made with a qualified
healthcare professional.
Regular Follow-ups

Regular appointments with your clinician is crucial to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to make necessary adjustments. Remember, everyone is unique, and what works best will depend on the individual’s symptoms, age, overall health, and personal response to treatment and therapies. It’s also recommended to maintain regular yearly follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
Disclaimer: ADHD Active provides ADHD assessment, diagnosis, and treatment services carried out by suitably qualified and regulated healthcare professionals. Services are delivered in line with recognised UK clinical guidelines. Content on this website is provided for informational purposes and does not replace individual clinical assessment or personalised medical advice.
